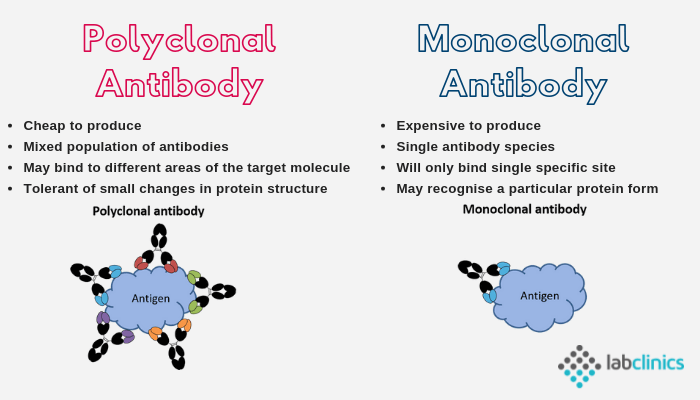
ADifference between monoclonal antibodies and polyclonal antibody was IPolyclonal antibodies pAbs are a collection of heterogeneous antibodies produced in the body by many B cell clones. Monoclonal antibodies provide higher specificity than polyclonal antisera because they bind to a single epitope and usually have high affinity.

An Overview Of Polyclonal And Monoclonal Antibodies Their Differences And How To Choose Goldbio
Monoclonal antibodies can cause side effects which can differ from person to person.

. The main difference between monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies is that monoclonal antibodies are produced by the same clone of plasma B cells and they bind to a unique epitope whereas polyclonal antibodies are produced by different clones of plasma B cells and they bind to the. There is a difference in the antibody recognition of an antigen and enzyme recognition of a substrate. It is a frequent misconception that monoclonal antibodies are better than polyclonal ones.
The ones you may have and how they make you feel will depend on many factors such as how healthy you are before treatment your type of cancer how advanced it is the type of monoclonal antibody you are receiving and the dose. Polyclonal antibodies are a heterogeneous antibody population. Polyclonal antibodies pAbs are antibodies that are secreted by different B cell lineages within the body whereas monoclonal antibodies come from a single cell lineage.
Antibodies utilized for research and symptomatic intentions are frequently obtained by infusing a lab creature like a rabbit or a goat with a particular antigen. Such a polyclonal response whose range of specificities and affinities can shift with time is ideal for combatting infection. They are a collection of immunoglobulin molecules that react against a.
B cells from the spleen of the immunized animal are then removed. Serum collected and immunoglobulin purified to eliminate serum proteins. The invading pathogen will be met by a barrage of antibody molecules capable of binding to many different sites on its surface.
A polyclonal antibody pAb is a collection of different monoclonal antibodies mAbs derived from different B cell lineages. Both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies interact with the same antigen. Monoclonal Antibody A monoclonal antibody refers to an antibody normally recognizing only a single antigen eg.
While the antibodies recognize in ground state the enzymes recognize in a transition state associated with a conformational change of protein. MAbs are currently used to treat cancer but their exorbitant cost has prevented them from being used more widely to treat. Each antibody in a pAb collection binds a specific epitope on the same antigen so it can increase sensitivity towards a specific antigen.
A single protein and within which only a single common epitope is recognized. In combination these antibodies exert a cumulative or synergistic effect which may explain the potent Dsg3-depleting capability of PV-IgG which is polyclonal. Can produce large quantities of identical antibody.
This therapy works best for people who face severe complications from SARS-CoV-2. In the last post about Antigen we mentioned that antigens are multivalent. They can recognize and bind to many different epitopes of a single antigen.
Monoclonal antibodies were approved as a COVID-19 treatment by the FDA last year and again in February and May. Polyclonal antibodies contain a heterogeneous combination of IgGs against the entire antigen though monoclonal antibodies production are made out of a solitary IgG against a single epitope. Antibodies produced in an animal in response to a typical antigen are heterogenous as they are formed by several different clones of plasma cells or called as polyclonal.
Individual monoclonal anti-Dsg3 antibodies display characteristic limits to their Dsg3-depleting activity which correlates with their pathogenic activities. Unlike polyclonal antibodies which are produced in live animals monoclonal antibodies are produced in vitro using tissue-culture techniques. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies Methods Mol Med.
Polyclonal Antibody A polyclonal antibody refers to an antibody normally recognizing only a single antigen but within which a number of different epitopes are recognized. Antibodies are generated by multiple B-cell clones more than one B-cell line 3-8 months 3. Animal immunized with antigen.
A short comment on the polyclonalmonoclonal issue. They have the ability to identify and bind to a variety of View the full answer. The antibody enzymes appropriately regarded as abzymes are the catalytic antibodies.
Monoclonal antibodies are typically produced by culturing antibody-secreting hybridomas derived from mice. Each individual antibody in a polyclonal mixture is technically a monoclonal antibody. Monoclonal antibodies are a homogeneous antibody population.
1-Complex mixture of antibodies directed against different epitopes and that differ in their affinity for the antigen cant easily easily manipulate via recombinant means 2-each antisera preparation differs in specificity average affinity cross reactive specifities 3- not optimised for application 4- supply is limited. In an analytical context often the opposite is the case. Polyclonal antibodies pAbs are mixture of heterogeneous which are usually produced by different B cell clones in the body.
However this term generally refers to a process by which the actual B-cell is isolated and fused to an immortal hybridoma cell line so that large quantities of identical antibody can be generated. MAbs are produced by immunizing an animal often a mouse multiple times with a specific antigen. Polyclonal antibodies are produced by injecting an immunogen into an animal.

Monoclonal And Polyclonal Antibody Differences Monoclonal Vs Polyclonal Antibody Youtube

An Overview Of Polyclonal And Monoclonal Antibodies Their Differences And How To Choose Goldbio
0 Comments